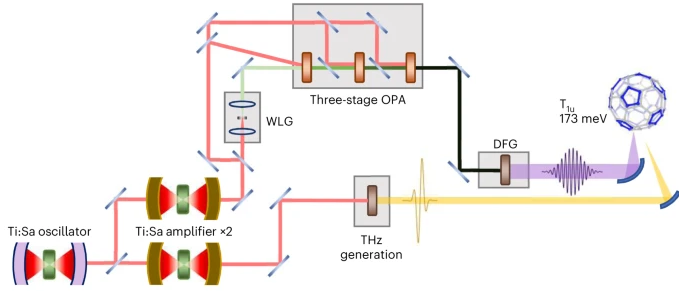
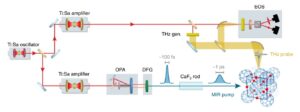
Photo-excitation at terahertz and mid-infrared frequencies has emerged as an effective way to manipulate functionalities in quantum materials, in some cases creating non-equilibrium phases that have no equilibrium analogue. In K3C60, a metastable zero-resistance phase was observed that has optical properties, nonlinear electrical transport and pressure dependencies compatible with non-equilibrium high-temperature superconductivity. Here we demonstrate a two-orders-of-magnitude increase in photo-susceptibility near 10 THz excitation frequency. At these drive frequencies, a metastable superconducting-like phase is observed up to room temperature. The discovery of a dominant frequency scale sheds light on the microscopic mechanism underlying photo-induced superconductivity. It also indicates a path towards steady-state operation, limited at present by the availability of a suitable high-repetition-rate optical source at these frequencies.
Reproduced with permission. Copyright 2023, Springer Nature




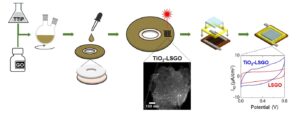
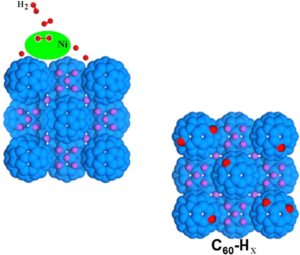 The addition of transition metals to alkali intercalated fullerides proved to enhance their already good hydrogen absorption properties. Herein we present a study based on two different synthetic strategies, allowing the addition of nickel as aggregates with different size to the lithium fulleride Li6C60: the former is based on the metathesis of nickel chloride, while the latter on the thermal decomposition of nickel carbonyl clusters. The hydrogen-storage properties of the obtained materials have been investigated with manometric and calorimetric measurements, which indicated a clear enhancement of the final absorption value and kinetics with respect to pristine Li6C60, as a consequence of nickel surface catalytic activity towards hydrogen molecules dissociation. We found up to 10 % increase of the total H2 weight % absorbed (5.5 wt% H2) in presence of Ni aggregates. Furthermore, the control of the transition metal particles size distribution allowed reducing the hydrogen desorption enthalpy of the systems.
The addition of transition metals to alkali intercalated fullerides proved to enhance their already good hydrogen absorption properties. Herein we present a study based on two different synthetic strategies, allowing the addition of nickel as aggregates with different size to the lithium fulleride Li6C60: the former is based on the metathesis of nickel chloride, while the latter on the thermal decomposition of nickel carbonyl clusters. The hydrogen-storage properties of the obtained materials have been investigated with manometric and calorimetric measurements, which indicated a clear enhancement of the final absorption value and kinetics with respect to pristine Li6C60, as a consequence of nickel surface catalytic activity towards hydrogen molecules dissociation. We found up to 10 % increase of the total H2 weight % absorbed (5.5 wt% H2) in presence of Ni aggregates. Furthermore, the control of the transition metal particles size distribution allowed reducing the hydrogen desorption enthalpy of the systems.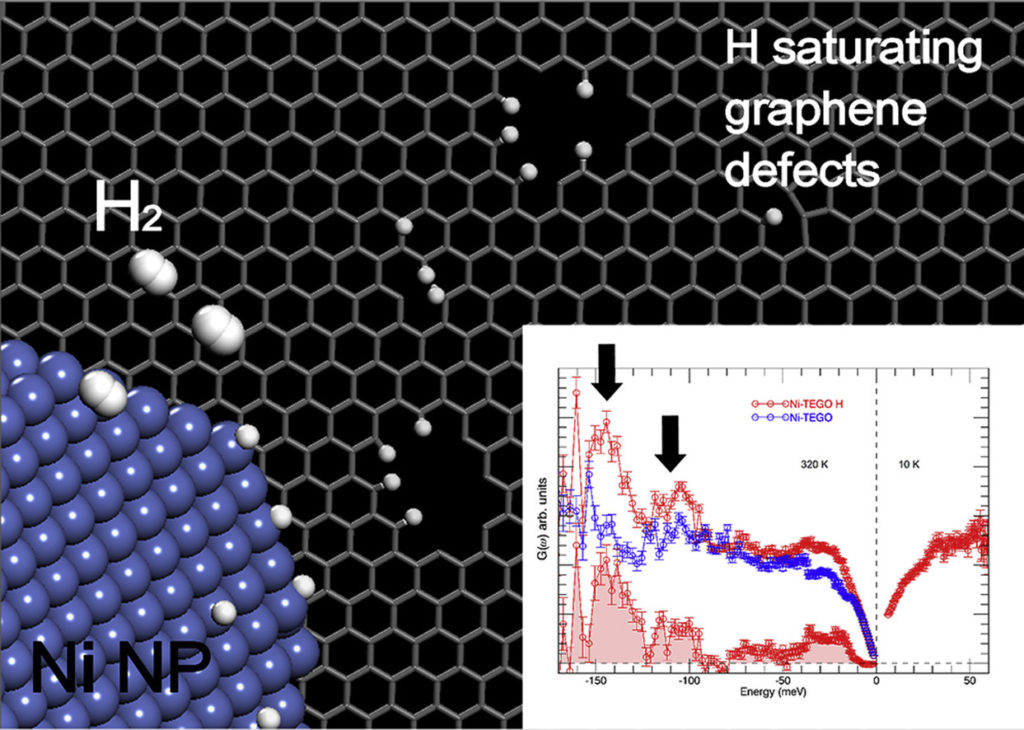 Surface decoration of graphene-based nanostructures with metals has been predicted to be an efficient way towards the development of resistant catalysts and novel materials for energy applications, such as hydrogen production and storage. We report on an extensive neutron scattering study of a defective graphene-based material decorated with nickel nanoparticles, obtained via the chemical decoration of thermally exfoliated graphite oxide. The combination of neutron diffraction and inelastic neutron scattering measurements has been used to characterize the low-dimensional carbon backbone and the presence of the nickel nanoparticles, organized at the nanometer scale on the graphene plane. The structural features of this system, along with the nickel capability of dissociating the hydrogen molecule upon hydrogen treatment, are herein discussed.
Surface decoration of graphene-based nanostructures with metals has been predicted to be an efficient way towards the development of resistant catalysts and novel materials for energy applications, such as hydrogen production and storage. We report on an extensive neutron scattering study of a defective graphene-based material decorated with nickel nanoparticles, obtained via the chemical decoration of thermally exfoliated graphite oxide. The combination of neutron diffraction and inelastic neutron scattering measurements has been used to characterize the low-dimensional carbon backbone and the presence of the nickel nanoparticles, organized at the nanometer scale on the graphene plane. The structural features of this system, along with the nickel capability of dissociating the hydrogen molecule upon hydrogen treatment, are herein discussed.