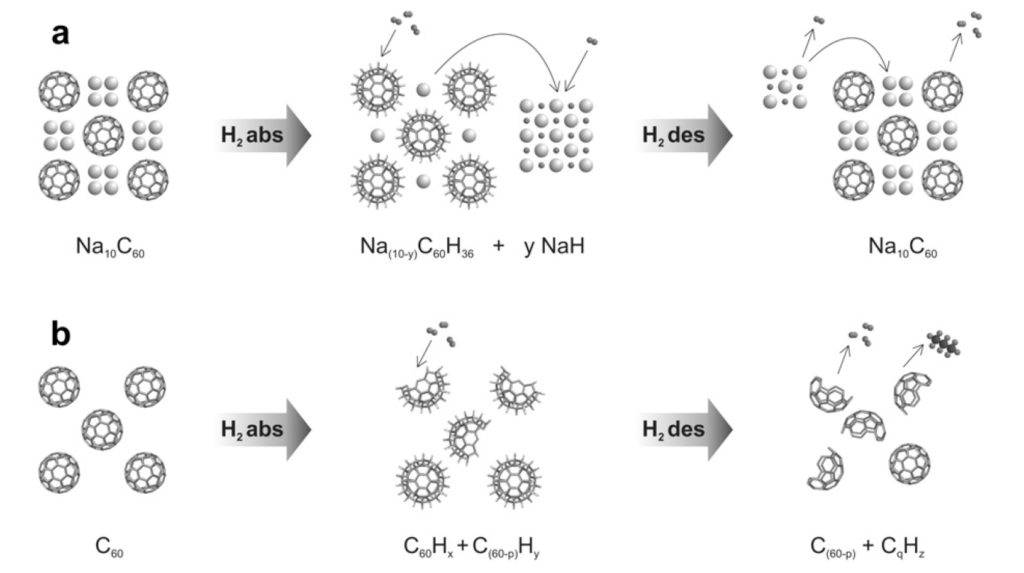
The hydrogen absorption of sodium intercalated fullerenes was determined and
compared to pure fullerenes C60. Up to 3.5 mass% hydrogen can reversibly be absorbed in NaxC60 at 200 C and a hydrogen pressure of 200 bar. The absorbed amount of hydrogen is significantly higher than for the case when only the sodium would be hydrogenated. At 200 bar the onset of hydrogen absorption is observed at 150 C. At a pressure of 1 bar hydrogen the major desorption starts at 250 C and is completed at 300 C. This absorption and desorption temperatures are significantly reduced compared to pure C60, either due to a catalytic reaction of hydrogen on sodium or due to the negatively charged C60. The hydrogen ab/desorption is accompanied by a partial de/reintercalation of sodium. A minor part of the hydrogen is ionically bonded in NaH and the major part is covalently bonded in C60Hx. The sample can be fully dehydrogenated and no NaH is left after desorption. In contrast to C60, where the fullerene cages for high hydrogen loadings are destroyed during the sorption process, the NaxC60 sample stays intact.
Reproduced with permission. Copyright 2012, Elsevier
